mechanics, topology, defects
This page contains supporting movies for the paper Topological soft modes bound to dislocations in mechanical metamaterials by Jayson Paulose, Bryan Gin-ge Chen, and Vincenzo Vitelli at the Instituut-Lorentz for theoretical physics, Leiden University. We demonstrate topologically protected mechanical motions associated with lattice defects called dislocations. The motion, localized to the region surrounding the defect in an otherwise rigid structure of stiff elements connected by free hinges, arises due to the interplay between two topological invariants, one characterizing the vibrations of the lattice and the other characterizing the size and orientation of the defect.
Video summary
I. Joint sample with two dislocations
Movie link |
Screenshot |
Description |
|
Supplementary movie 1 Bulk rigidity |

|
The movie shows a network of rigid triangles joined by free pivots at their vertices, and pinned at the boundaries. Green and orange triangles highlight the position and orientation of a dislocation, of which there are two in the structure. The lattice structure is such that the network is rigid in the bulk (white triangles): the acoustic phonon modes are gapped. |
|
Supplementary movie 2 Localized motion at left dislocation |

|
Although points away from the left dislocation cannot be moved, points in the vicinity of the dislocation can be moved, albeit in a specific, collective manner. |
|
Supplementary movie 3 Motion at left dislocation and its absence at right dislocation |

|
In contrast to the dislocation on the left, the right dislocation does not harbour a soft motion and the network is rigid at points in the neighbourhood of the dislocation. |
II. Separated dislocations
Movie link |
Screenshot |
Description |
|
Supplementary movie 1 Bulk rigidity |
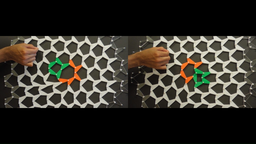
|
The movie shows two networks (A on the left; B on the right) of rigid triangles joined by free pivots at their vertices, and pinned at the boundaries. Green and orange triangles highlight the position and orientation of a dislocation within each structure. The lattice structure is such that both networks are rigid in the bulk (white triangles): the acoustic phonon modes are gapped. |
|
Supplementary movie 2 Localized motion in network A |

|
Although points away from the dislocation in network A cannot be moved, points in the vicinity of the dislocation can be moved, albeit in a specific, collective manner. |
|
Supplementary movie 3 Motion in network A and its absence in network B |

|
In contrast to network A (on the left), network B (right) is completely rigid everywhere including at points in the neighbourhood of the dislocation. |